Introduction
Understanding real estate tax deductions is important for a real estate investor looking to maximise capital and return on investment. These tax cuts can have a significant impact on investments, so it’s important to stay informed.
1) Key Tax Deductions for Rental Properties
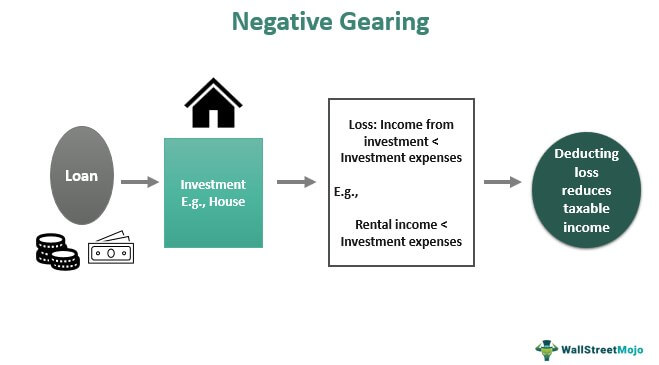
1.1 Negative Gearing
One of the most useful rental property tax deductions available to investors is negative gearing.
Investment assets are negatively valued when interest earnings, or rental income, are less than the cost of the assets. Essentially, this means that the asset is making a loss and cash flow is negative. This provides a significant tax advantage because the owner can claim the loss as a tax deduction to offset his taxable income.
1.2 Cleaning Expenses
Rental property owners can claim tax deductions for cleaning costs associated with their property. This includes the cost of professional cleaners and the purchase of supplies for the property. Regular maintenance is necessary to maintain the appeal of the rental property and ensure that it remains intact.
1.3 Council Rates
Local government and council rates for rental houses are 100% tax deductible. These fees are normally paid once a year and fund garbage collection, roadway maintenance, and other community services. By claiming this number as a tax deduction, investors can lower their taxable income while increasing their overall return on investment.
1.4 Gardening and Lawn Mowing
Taxes are paid to maintain the gardens and lawns on the rental property. This includes the expense of employing professional landscapers as well as the purchase of gardening tools and equipment. Regular upkeep is required to protect the property value and attract new tenants.
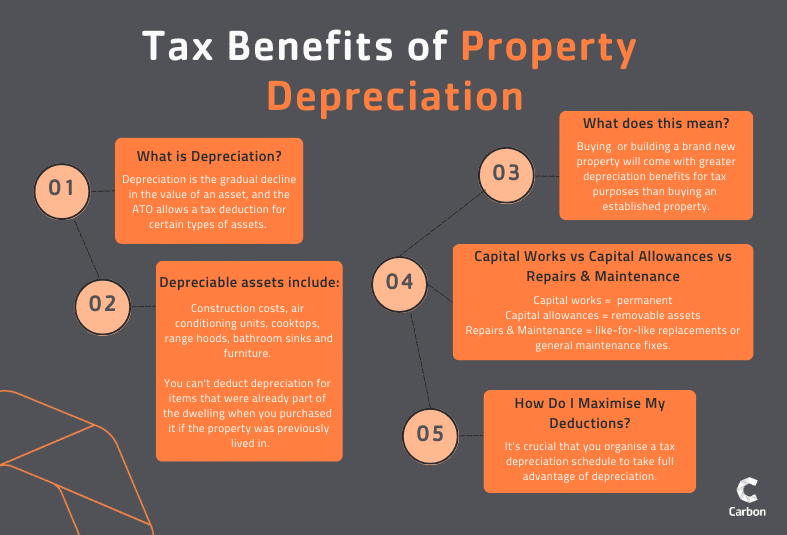
1.5 Depreciation
Depreciation is a significant tax deduction for rental property owners. The property’s fixtures, fixtures, and items lose value over time due to wear and tear. Investors might reduce their taxable income and increase their returns by depreciating these assets. It is critical that a certified quantifier create a tax deduction schedule to appropriately account for these deductions.
2) Additional Tax Deductions
2.1 Landlord Insurance Premiums
Insurance expenses for the protection of foreclosed property are tax deductible. This includes homes insurance, which protects property owners against losses due to tenant default, property damage, and legal fees. Premiums can be claimed as tax deductions by investors, lowering their taxable income and better protecting their investments.
2.2 Mortgage Interest
Interest on mortgages is taxable. This can result in significant tax savings for investors, especially in the early years of a mortgage when the majority of the payments are for interest. By claiming this deduction, investors can lower their taxable income and increase their returns.
2.3 Leasing Commissions
Taxes paid to real estate agents for finding tenants are fully deductible. These premiums are often a percentage of rental income and are due when a new tenant signs the lease. By claiming this investment as a tax deduction, the taxable income can be lowered while also covering the cost of property transfer.
2.4 Maintenance Costs
Regular rentals are tax deductible. This includes the expense of minor initiatives such as painting and upkeep that are required to keep the property in its prime state. By claiming these charges as tax deductions, investors can minimise taxable revenue while ensuring renters’ assets remain intact.
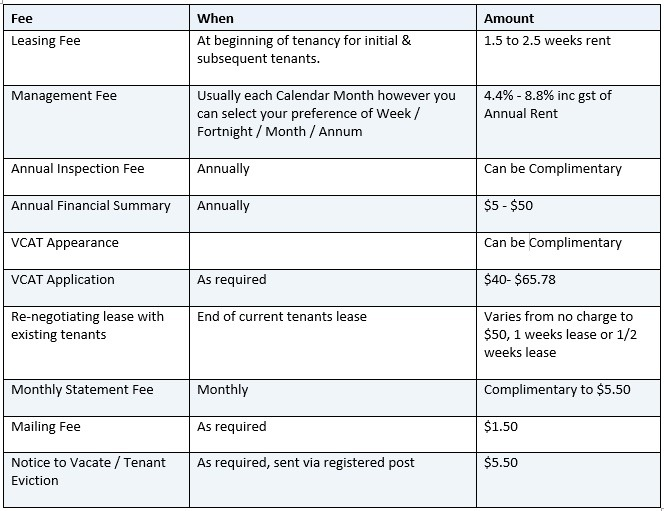
2.5 Property Management Fees
Property managers are taxed to maintain their rental properties. Among the duties performed by property managers are finding renters, arranging maintenance, and collecting rent. Investors can minimise their taxable income and ensure the proper management of their assets by claiming these amounts as tax deductions.
Below is a simple diagram of the fees, how much to expect from each payment, and how often.
3) Reporting and Filing
3.1 Schedule E
Rental income and expenses must be reported on Schedule E for tax purposes. This form is used to report income and expenses for rental property and to file the investor’s annual tax returns. By accurately reporting these figures, investors can ensure that all applicable tax deductions are claimed and potential audits or penalties are avoided.
3.2 Form 4562
Form 4562 is used to calculate rental property depreciation and premium deductions. This form is sent to the investor’s annual tax return and is necessary to accurately claim depreciation deductions. Consulting a tax professional or quantity surveyor is important to ensure accurate information is reported on this form.
3.3 Expense Tracking
Landlords must keep detailed records and receipts to support tax deductions. This includes receipts for property charges, records of rental income, and information about tenants. By keeping accurate records, investors can ensure they are claiming all applicable tax deductions and providing the necessary documentation if they are checked by the tax authorities.
In Conclusion
Maximising rental property tax deduction is essential to improving the economic returns on investment properties. By having deduction reasons in place and accurate record keeping, investors can significantly reduce their taxable income and improve their cash flow It is important to consult a tax professional or a financial advisor to ensure that all applicable deductions have been claimed and remain abreast of any changes in tax laws or regulations.
For more expert insights and helpful resources, follow Success Avenue Property Consulting on our social media and reach out to us today at 02-81230180, info@successavenue.com.au | www.successavenue.com.au

